Concussions on Prezi
Friday, February 3, 2012
Wednesday, December 21, 2011
EMG Lab
EMG Lab:
What is EMG? EMG is a graphical recording of electrical activity within the muscles.
When the muscles are activated by nerves it results in changes in ion flow across cell membranes. This generates electrical activity. During this lab, we tested the electrical activity within the muscles of your jaw while eating different types of food, varying in hardness.
Hypothesis:
If we differ the hardness in foods, then the jaw muscles will show more electrical activity because the jaw works harder to chew harder foods then it does softer things.
Materials:
EKG probe and electrode tabs
Different types of food
Mouth :) (Someone to eat)
Experiment:
We hooked up Sierra to the probes to study her electrical activity. She had probes on her upper and lower jaw. First, we had a baseline (Sierra clenched her jaw and recorded the activity). Sierra rested her jaw for 5 seconds between each different types of food. We then gave her 8 different types of food (pudding, BBQ chips, carrots, chocolate chip cookies, a banana, celery, Dr. Pepper, & beef jerky)
Results:
Analysis:
As you can see, different types of food had different types of activity. The average activity was o.5 mV. The highest, surprisingly, was pudding with 2.2mV. We believe that the pudding had the highest amount of activity because the jaw moves more while trying to swallow the pudding because you don't have to chew as much. The lowest activity was Dr. Pepper. We believe this was because drinking liquids don't involve much of any activity.
Conclusion:
We can conclude that our hypothesis is sometimes true, but not always. Celery is in fact harder then things such as Dr. Pepper, but this is not the case with celery and pudding. Even though our hypothesis was partially incorrect, we had a great time conducting the lab and actually learned a lot!!
Friday, December 16, 2011
Research - Muscle Regeneration :)
What are muscles responsible for?
40% of our body mass!
breathing
eating
posture
walking
reflexes
heat generation
metabolism
Muscle loss is called - atrophy or wasting
Muscle loss causes:
disuse
injury
starvation
diseases such as cancer
sepsis
neuromuscular disorders
ageing
Muscle mass is reduced about 1/3 when humans reach the age of 50-80
The University of Western Australia
has researched many things about muscles.. not only how they affect they body and also the heart as well
They took aged mice and this was exactly what they did!!
SOURCE: (http://www.anhb.uwa.edu.au/research/student-projects/muscle-regeneration)
Weights – Body weights, muscle weights
- Levels of muscle IGF-1 in young and old transgenic mice (IGF-1 elisa)
- Muscle fibre type changes (Immunostaining)
- Myofibre number and size (cross-sectional area) changes (HandE staining)
- Neuromuscular Junctions – morphology and innervation (Immunostaining and Imaging on Confocal lazer microscope)
- Motoneuron counts in the spinal cord (toluidine blue staining/developing other methods)
- Oxidative stress measurements
- Levels of neurotrophic factors (qPCR/mRNA levels/Western Blots)9. Signalling pathways – Phosphoprotein signalling (Western Blots)
Thursday, December 15, 2011
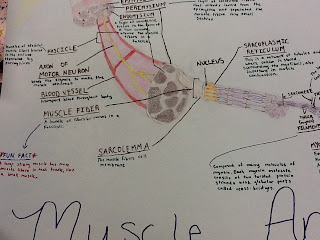
Muscle Anatomy!
While learning Muscle Anatomy, we broke ourselves up into different groups (Me, Madison, Chapin) to create our own version of Muscle Anatomy! It worked out very well actually. Here is our creation below!
Each group worked on Muscle Anatomy, Sliding Filament Theory (How we think muscles contract!), or Neuromuscular Junction.
Obviously, like said before, we worked on Muscle Anatomy!
The Big Picture!
& below are different sections up close!
Tuesday, November 15, 2011
Monday, October 31, 2011
Integumentary System
Click the link below to go to my Glog!
Then.....
Click on the Epidermis & Dermis boxes for more information (:
http://adavis93.glogster.com/glog/
What makes your skin color?
Melanin - yellow to black pigment. This makes skin color dark or light
Freckles result from accumulations of melanin
Carotene - yellow to orange. found in the palms and feet
Hemoglobin- reddish. makes skin pinkish
Sweat glands! Prevent overheating of body
Eccrine - palms, feet, forehead
Apocrine - axillary and anogenital areas
Ceruminous - ear canal
Mammary - secrete milk
Sebaceous -
found all over body
soften skin when hormones stimulate
oily secretion
responsible for acne
HAIR!
Dead keratinized cells
hard keratin
contains a medulla, cortex, cuticle
melanocytes determine color
FUNCTIONS-
maintain warmth
alert insects on skin
guarding scalp against sunlight, heat, and trauma
--We do not have hair on our palms, soles, and lips
Alopecia- hair thinning
Functions of Integumentary-
Protection
body temp regulation
dilation and constriction of dermal vessels
Cutaneous sensation
Metabolic functions - vitamin D
blood reservoir - 5% of blood volume
Excretion
Skin Cancer -
Three major types: Basal - most common, least dangerous.. surgical excision
Squamous- found on scalp, ears, lower lip. grows rapidly
Melanoma (rare but most dangerous) - resistant to chemo
use the ABCD rule
A: asymmetry
B: border
C: color
D: diameter
BURNS:
First degree- only the epidermis is damaged (redness, swelling, pain)
Second degree - epidermis & upper dermis (blisters)
Third degree - entire skin (appears gray-white, no pain)
Rule of 9's
estimates severity
considered critical if----
over 25% - second degree
over 10% third degree
third degree on face, hands, or feet
Then.....
Click on the Epidermis & Dermis boxes for more information (:
http://adavis93.glogster.com/glog/
What makes your skin color?
Melanin - yellow to black pigment. This makes skin color dark or light
Freckles result from accumulations of melanin
Carotene - yellow to orange. found in the palms and feet
Hemoglobin- reddish. makes skin pinkish
Sweat glands! Prevent overheating of body
Eccrine - palms, feet, forehead
Apocrine - axillary and anogenital areas
Ceruminous - ear canal
Mammary - secrete milk
Sebaceous -
found all over body
soften skin when hormones stimulate
oily secretion
responsible for acne
HAIR!
Dead keratinized cells
hard keratin
contains a medulla, cortex, cuticle
melanocytes determine color
FUNCTIONS-
maintain warmth
alert insects on skin
guarding scalp against sunlight, heat, and trauma
--We do not have hair on our palms, soles, and lips
Alopecia- hair thinning
Functions of Integumentary-
Protection
body temp regulation
dilation and constriction of dermal vessels
Cutaneous sensation
Metabolic functions - vitamin D
blood reservoir - 5% of blood volume
Excretion
Skin Cancer -
Three major types: Basal - most common, least dangerous.. surgical excision
Squamous- found on scalp, ears, lower lip. grows rapidly
Melanoma (rare but most dangerous) - resistant to chemo
use the ABCD rule
A: asymmetry
B: border
C: color
D: diameter
BURNS:
First degree- only the epidermis is damaged (redness, swelling, pain)
Second degree - epidermis & upper dermis (blisters)
Third degree - entire skin (appears gray-white, no pain)
Rule of 9's
estimates severity
considered critical if----
over 25% - second degree
over 10% third degree
third degree on face, hands, or feet
Wednesday, October 19, 2011
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)